Real Tips About How To Stop Gi Bleeding

Summary of the management of upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
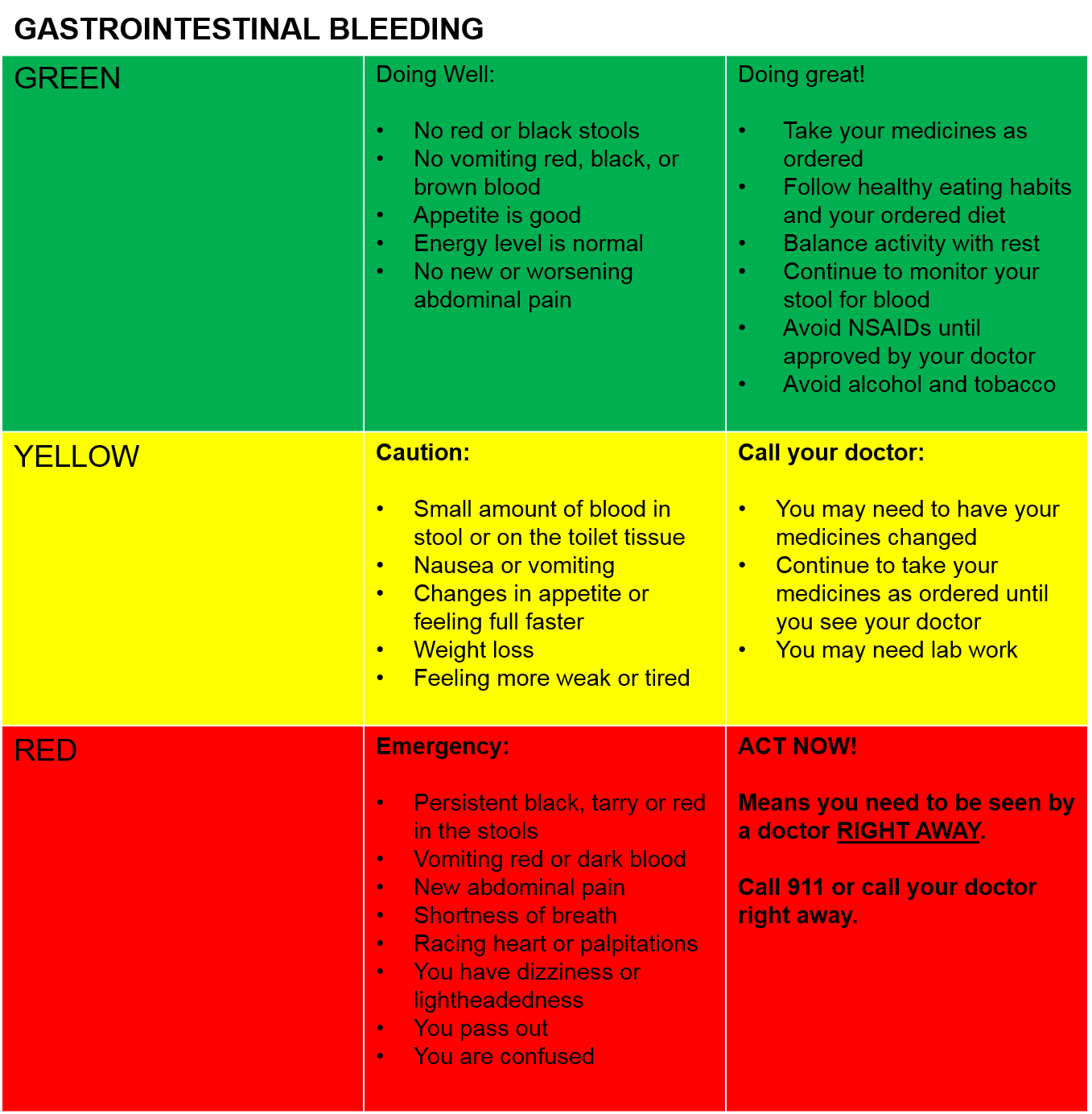
How to stop gi bleeding. Bleeding in the digestive tract is a symptom of a problem rather than a disease itself. Gi bleeding may occur in any part of your digestive tract. If you have bleeding in your gastrointestinal tract, you may experience blood in your stool or stool that is darker and sticky.
You can prevent some of the causes of bleeding in your gi. Causes and treatments. If you have had bleeding from peptic ulcers or gastritis, you can help prevent gi bleeding by avoiding alcoholic drinks and smoking.
How to treat upper gastrointestinal bleeding: Alcohol and smoking can increase stomach acids. Symptoms & causes of gi bleeding.
1.2.1 do not offer blood transfusion to patients with acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding who have a haemoglobin level of more than 0.8 g/litre, unless there is another indication. Upper gastrointestinal (gi) bleeding refers to bleeding that occurs anywhere in the esophagus, the stomach, or the upper. For example, it's sometimes possible to treat a bleeding peptic ulcer during an upper endoscopy or to remove polyps during a.
Doctors can prevent gi bleeding by treating the conditions that cause the bleeding. If it doesn't, treatment depends on where the bleed is from. Symptoms of gastrointestinal (gi) bleeding.
What do i need to know about gastrointestinal (gi) bleeding? What causes gastrointestinal bleeding and how serious is it really? In many cases, bleeding can be treated with medicine or a procedure during a test.
Bleeding may occur anywhere along the digestive (gastrointestinal or gi) tract, from the mouth to the anus. A lower gastrointestinal (gi) bleed can happen as a result of an injury, ulceration, or. 1 recognizing the signs stabilizing vital signs.
How can i prevent gi bleeding? Hemodynamic assessment and resuscitation as needed. What are the symptoms of gi bleeding?
Despite the bleeding risk, dual antiplatelet therapy (dapt), consisting of aspirin with a p2y12 inhibitor, remains the cornerstone of treatment in patients with. Often blood transfusions are not recommended unless the. Gastrointestinal (gi) bleeding is a symptom of a disorder in your digestive.
One of the newer gastroenterologists on staff did an egd and found grade 3 esophageal varices with stigmata of prior hemorrhage but were not actively bleeding. Gibleeding often stops on its own. Steps you can take to protect yourself against gi bleeding include: